London | February 2, 2026 – The World Shipping Council (WSC) shared today the latest update on the global dual-fuel fleet, revealing a massive structural shift in maritime investment. As of February 2026, the data confirms that the liner industry has moved aggressively from planning to execution. With $150+ billion already committed, the dual-fuel fleet is no longer a “future project”, it is the new operational standard for global trade.
Table of Contents
At a Glance:
- Latest Data: World Shipping Council (WSC) Dual-Fuel Fleet Dashboard (Feb 2026 Update).
- Fleet Status: 400 vessels active; 1,126 total vessels delivered or on order ($150B+ investment).
- Regulatory Focus: Support for the IMO Net-Zero Framework to address the 3–4x price gap in green fuels.
- Market Lead: Container and vehicle carriers are the primary drivers, with 74% of the combined order book now dual-fuel.
As of early 2026, the maritime industry has moved from “theoretical decarbonization” to “operational de-risking.” With 400 dual-fuel vessels active and over 1,000 projected by 2030, the bunkering industry faces an immediate mandate to bridge the “green fuel gap” through infrastructure scaling and global regulatory support.
The Dual-Fuel Evolution: Tracking the Liner Shipping Industry’s Path to Net-Zero
A Strategic Pivot in Global Maritime Investment
The global shipping industry is undergoing a structural realignment, moving beyond the exploration of lower-emission alternatives toward a decisive, market-wide de-risking strategy. Central to this transition is the adoption of dual-fuel technology, vessels engineered to operate on both conventional fuels and renewable alternatives.
This capability serves as the industry’s primary strategic bridge to the 2050 net-zero target. The World Shipping Council (WSC) remains committed to this goal, recognizing that as a greenhouse gas emitter, the shipping industry must do its part to combat the catastrophic effects of climate change. The data and insights presented here are derived from the WSC Dual-Fuel Fleet Dashboard as of the December 2025 update.
The Surge in Operational Capacity
In the bunkering sector, “ships on the water” is the most critical metric for assessing immediate infrastructure needs. While the order book signals future intent, the active fleet represents real-time energy demand and operationalized technology.
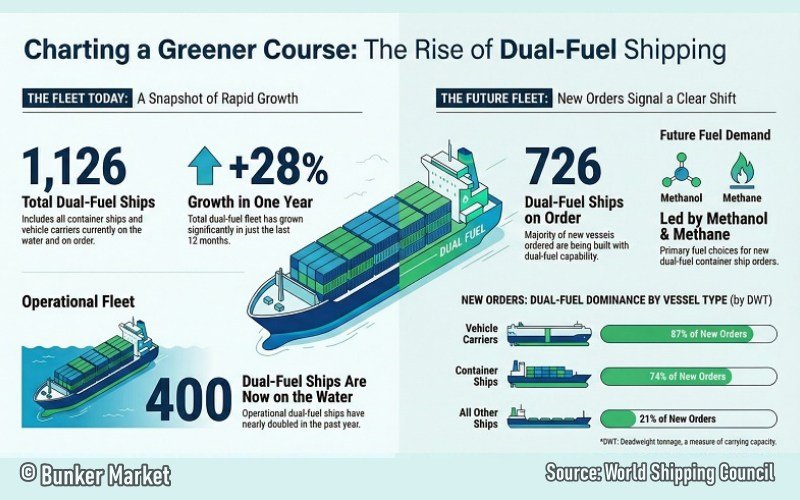
The WSC data confirms a significant acceleration:
- December 2024: 218 dual-fuel container ships and vehicle carriers in service.
- December 2025: 400 vessels in service.
This 182-vessel increase in a single year represents an 83% surge. This momentum is not slowing down; the WSC projects that over 1,000 dual-fuel ships will be on the water by 2030, all capable of running on the cleanest fuels available.
The Order Book: Analyzing the Dual-Fuel Pipeline
The “order book” serves as the industry’s leading indicator for long-term fuel procurement and trade resilience.
Dual-Fuel Fleet Growth (Dec 2025)
| Fleet Category | Number of Units | Year-over-Year Change |
| Ships in Service | 400 | +83.5% |
| Ships on Order | 726 | +6.4% |
| Total Dual-Fuel Fleet | 1,126 | +28% |
The total investment in these vessels now exceeds $150 billion. Shipowners are essentially locking in the technical capacity to utilize green fuels well before the fuels themselves are available at scale, demonstrating a sophisticated approach to global trade resilience.
Sector-Specific Dominance: Containers and Vehicle Carriers
The adoption of dual-fuel technology reveals a widening gap between the liner shipping industry and the broader maritime market. Container ships and vehicle carriers are the undisputed vanguards.
When evaluating the order book by Deadweight Tonnage (DWT):
- Container ship orders: 74% are dual-fuel.
- Vehicle carrier orders: 87% are dual-fuel.
- Rest of the global fleet: Only 21% are dual-fuel.
This high concentration indicates that the first regional “green hubs” will naturally emerge at ports that serve these specific high-capacity liner routes.
The Policy Mandate: Bridging the Green Fuel Gap
While the fleet is ready, a massive economic hurdle remains. Container and vehicle carriers are already operating vessels capable of running on the greenest fuels, but these fuels currently cost 3 to 4 times more than conventional options, and supply needs to be drastically scaled.
“Liner shipping has already moved to kick-start decarbonization. However, a global regulation is necessary to deliver the renewable fuels at a commercially viable price.” – Joe Kramek, WSC President and Chief Executive Officer
The IMO Net-Zero Framework
The WSC supports the IMO Net-Zero Framework, a global agreement designed to:
- Incentivize fuel providers to invest in new production capacity.
- Level the playing field by applying emissions plans fairly and globally across the sector.
- Set ambitious targets, including a 65% reduction in emissions by 2040 and reaching net-zero around 2050.
Future Fuel Demand: Methanol and Methane
WSC data reveals that 78% of container ship capacity (by TEU) on order is dual-fuel. This demand is currently consolidating around two primary pathways: methanol and methane (LNG).
The dominance of these fuels necessitates a rapid diversification of the global bunkering landscape. Suppliers can no longer rely on traditional fuel oil infrastructure; they must scale their ability to provide methanol and methane to meet the energy needs of the next generation of liner shipping.
The Roadmap to 2050
The December 2025 WSC Dual-Fuel Fleet Dashboard provides a definitive roadmap for the industry’s decarbonization journey. The critical takeaways are:
- Accelerated Execution: The doubling of the active dual-fuel fleet in one year proves the industry is operationalizing its commitments.
- Global Regulation is Key: To bridge the 3–4x price gap of green fuels, the IMO Net-Zero Framework is the essential tool for commercial viability.
- Infrastructure Readiness: With 1,000+ ships coming by 2030, the “green fuel gap” is the next great hurdle for energy providers.
About the World Shipping Council
The World Shipping Council (WSC) is the united voice of the liner shipping industry, representing container and vehicle carriers that account for roughly 90% of global liner capacity.
As a non-profit trade association with offices in Washington, Brussels, London, and Singapore, the WSC partners with governments and stakeholders to tackle the industry’s most pressing challenges. Their core mission focuses on:
- Decarbonization: Leading the path to net-zero emissions by 2050 through global regulations and international R&D.
- Security & Safety: Enhancing maritime security and cargo integrity without impeding the free flow of commerce.
- Trade Facilitation: Advancing policies that ensure efficient global transportation infrastructure and supply chain resilience.
Source: World Shipping Council